6G Design with ISAC & MATLAB
Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) in 6G Networks
6G represents a major leap forward in wireless communication, aiming to deliver highly customized user experiences by incorporating advanced radar technologies for precise localization. This advancement enables a closer integration of location-aware services with communication infrastructure, significantly improving both service quality and network performance.
This innovative approach, known as integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), combines radar and communication functions to create more efficient and responsive connectivity. Understanding ISAC is key to recognizing how 6G will provide smarter, more adaptive network services tailored to individual needs.
Future-facing technologies such as autonomous transportation, smart urban environments, and next-generation healthcare will depend heavily on the fusion of ultra-fast data exchange with accurate environmental sensing. These use cases highlight the critical role of ISAC in enabling a seamless, intelligent, and interconnected digital ecosystem.

Explore ISAC Algorithms with MATLAB
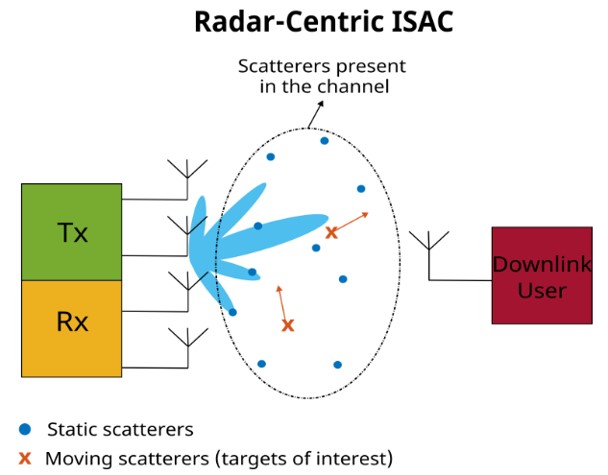
The example here demonstrates the modeling of an Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) system focused on radar, utilizing a MIMO radar that transmits a phase-modulated continuous wave (PMCW) signal.
MIMO-OFDM Communication-Centric iSAC
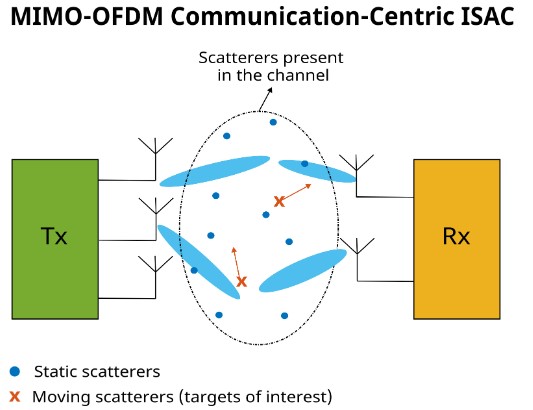
The example here illustrates how to design a communication-focused Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) system using a generic MIMO-OFDM communication framework.
ISAC using 5G NR Signals
In this video example, MATLAB’s advanced features are employed to track a moving object by passively utilizing reflected cellular signals. This approach enables simultaneous estimation of the object’s position and velocity, along with decoding the signals at the receiver.”
Prototype ISAC Algorithsm on USRP

This demonstration guides you through analyzing algorithm behavior and evaluating Range-Doppler performance, followed by leveraging FPGA code generation to seamlessly transfer portions of the design to an NI USRP device. With just a few lines of code, data can be exchanged between MATLAB on the host and the NI USRP FPGA
